

1), to reinforce the capsule during external rotation and extension. The iliofemoral ligament is composed of lateral (superior) and medial (inferior) fibrous branches, which insert together into the anterior inferior iliac spine of the pelvis, each extending out to attach along the femoral intertrochanteric line, forming the inverted Y-shaped ligament of Bigelow ( Fig. The hip joint itself is reinforced by 3 primary fibrous capsular ligaments (iliofemoral, ischiofemoral, and pubofemoral), and each serves distinct functional roles to stabilize the joint 5, 8. Within the hip joint, higher ratios of type-III collagen in the ligamentous capsule are associated with hip instability 23, 24, whereas elevated levels in the cartilage are associated with progressive joint degeneration 25, 26. Human ligaments consist of predominantly type-I collagen (85%) and combinations of type III, V, VI, XI, and XIV (15%) 21, 22. The purpose of this review was to provide a comprehensive summary of the functional anatomy and material characteristics of the hip capsule and the effects of different capsular management techniques during arthroscopic and arthroplasty procedures on joint function. Several recent laboratory studies have provided new insights into functional mobility and stability of the hip joint that should be carefully considered during surgery 9 - 20. More importantly, how the hip capsule is managed during surgical interventions (preservation and arthroplasty) and its effects on joint function are increasingly recognized 5 - 8. Although the anatomy of hip capsular ligaments has been well described in the literature 1 - 4, the knowledge of its characteristics and contributions toward hip mechanics and disease processes are evolving.
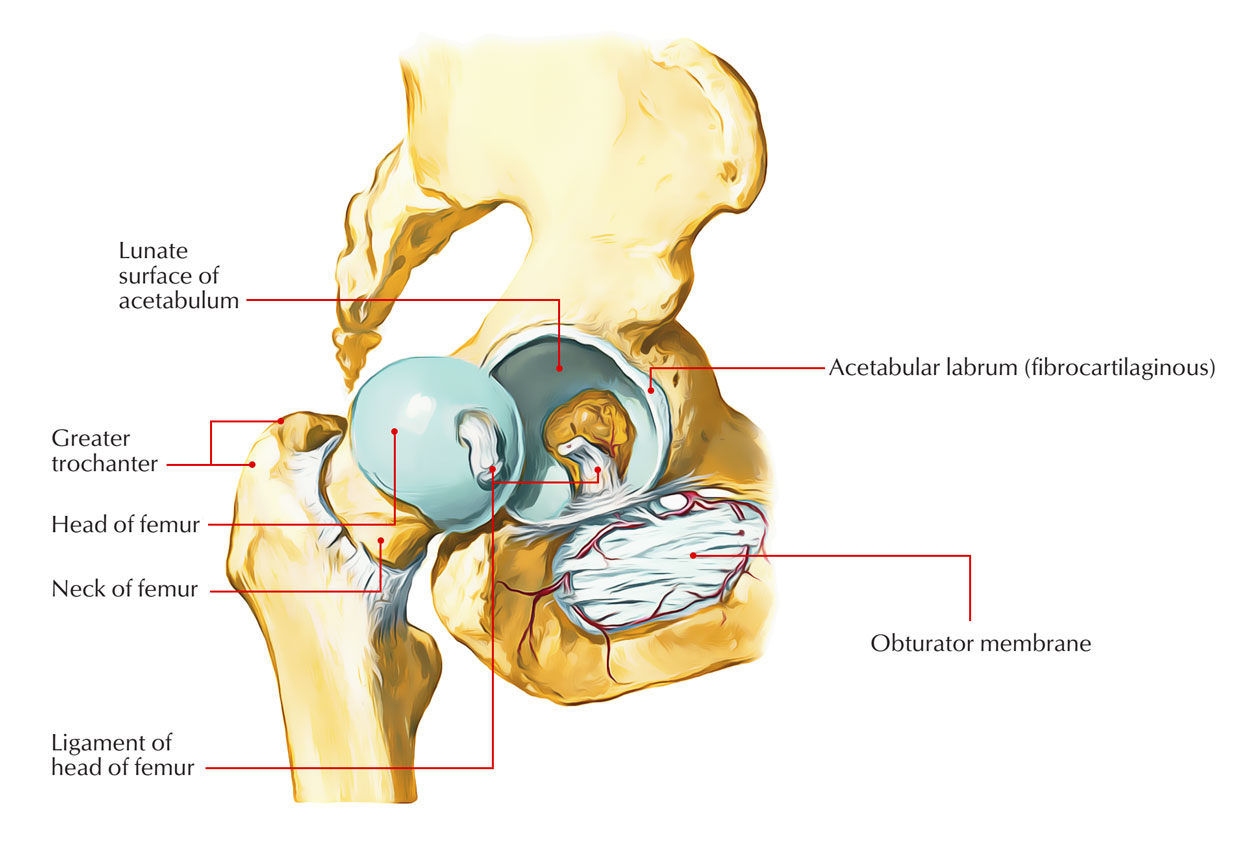
Hip joint capsular ligaments serve a fundamental role in balancing functional mobility and joint stability.
Complete anatomy of hip joint license#
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CCBY), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. On the Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest forms, which are provided with the online version of the article, one or more of the authors checked “yes” to indicate that the author had a relevant financial relationship in the biomedical arena outside the submitted work ( ).

Investigation performed at the Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom, and the Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, Canadaĭisclosure: The authors indicated grant support from the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) (EP/K027549/1 and EP/N006267/1) and the Wellcome Trust (088844/Z/09/Z), during the conduct of the study. 1MSk Lab, Department of Surgery and Cancer, Imperial College London, London, United KingdomĢDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, Imperial College London, London, United KingdomģDivision of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario, CanadaĮmail address for P.E.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
